In R, the break and next statements are control flow statements used within loops to control the flow of execution.
We can alter a normal looping sequence using the break or the next statement. Let's learn about them in detail.
break Statement
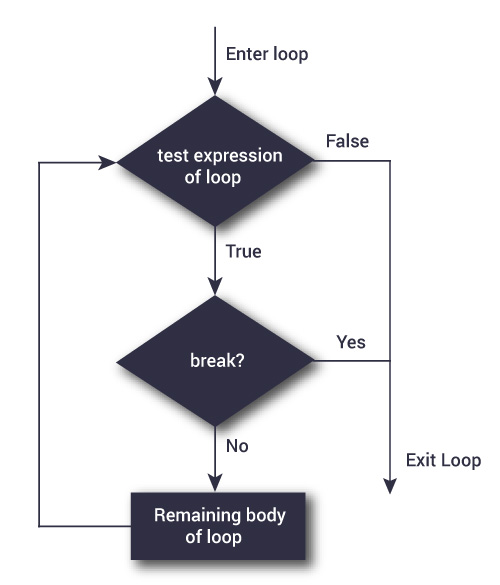
A break statement is used inside a loop (repeat, for, while) to stop the iterations and flow the control outside of the loop.
In a nested looping situation, where there is a loop inside another loop, this statement exits from the innermost loop that is being evaluated.
Syntax of break Statement
The syntax of the break statement is:
if (test_expression) {
break
}
Here, test_expression is evaluated. If it results in a logical value of TRUE, the break statement is executed.
When the break statement is encountered, the loop in which it resides is terminated, and the program continues with the next statement after the loop.
Note: The break statement can also be used inside the else branch of if...else statement.
Flowchart of break statement
Example 1: break statement
x <- 1:5
for (val in x) {
if (val == 3){
break
}
print(val)
}
Output
[1] 1 [1] 2
In this example, we iterate over the vector x, which has consecutive numbers from 1 to 5.
Inside the for loop we have used a if condition to break if the current value is equal to 3.
As we can see from the output, the loop terminates when it encounters the break statement.
next Statement
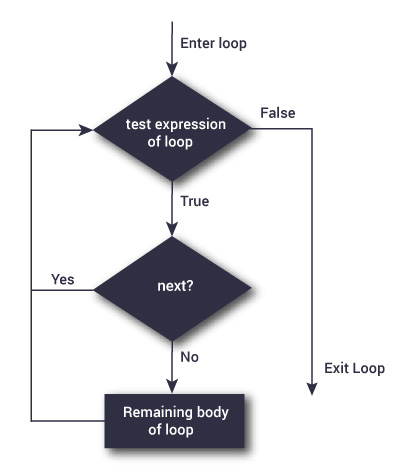
A next statement is useful when we want to skip the current iteration of a loop without terminating it.
On encountering next, the R parser skips further evaluation and starts the next iteration of the loop.
Syntax of next Statement
if (test_condition) {
next
}
Here, test_condition is evaluated. If it results in a logical value of TRUE, the next statement is executed.
When the next statement is encountered, the current iteration of the loop is skipped, and the program moves to the next iteration of the loop.
Note: The next statement can also be used inside the else branch of if...else statement.
Flowchart of next statement
Example 2: Next statement
x <- 1:5
for (val in x) {
if (val == 3){
next
}
print(val)
}
Output
[1] 1 [1] 2 [1] 4 [1] 5
In the above example, we use the next statement inside a condition to check if the value is equal to 3.
If the value is equal to 3, the current evaluation stops (value is not printed) but the loop continues with the next iteration.
The output reflects this situation.